Lewis Dot Structure For C3h4
Ready to learn how to describe the lewis construction of C3H8?
Awesome!
Here, I accept explained six elementary steps to depict the lewis dot construction of C3H8 (forth with images).
So, if yous are ready to go with these half-dozen simple steps, then permit's swoop correct into it!
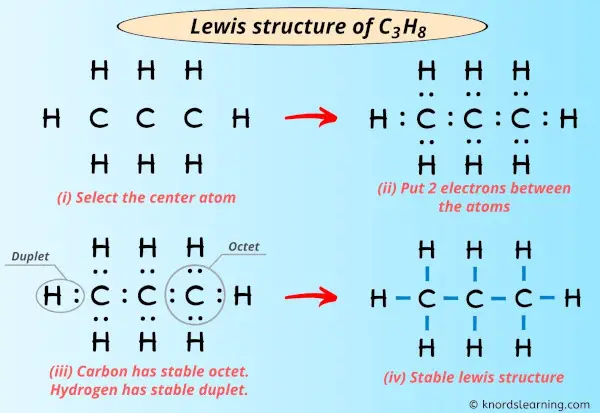
Lewis structure of C3H8 (or Propane) contains single bonds between Carbon-Carbon atoms as well as betwixt Carbon-Hydrogen atoms. The three Carbon atoms (C) are at the middle and they are surrounded by Hydrogen atoms (H).
Let's depict and understand this lewis dot construction step by step.
(Note: Take a pen and paper with yous and try to draw this lewis construction along with me. I am certain you will definitely learn how to draw lewis structure of C3H8).
6 Steps to Depict the Lewis Structure of C3H8
Footstep #1: Calculate the full number of valence electrons
Here, the given molecule is C3H8 (propane). In guild to draw the lewis construction of C3H8, first of all y'all take to find the total number of valence electrons present in the C3H8 molecule.
(Valence electrons are the number of electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom).
So, permit'south summate this first.
Adding of valence electrons in C3H8
- For Carbon:
Carbon is a group 14 element on the periodic tabular array.
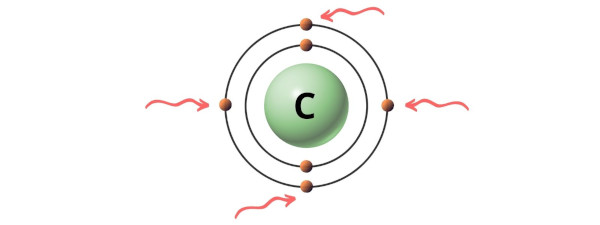
Hence, the valence electrons present in carbon is 4 (see below paradigm).
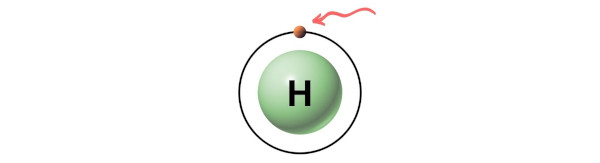
- For Hydrogen:
Hydrogen is a group 1 element on the periodic table.
Hence, the valence electron present in hydrogen is i (see below epitome).
Hence in a C3H8 molecule,
Valence electrons given by Carbon (C) atom = 4
Valence electron given by each Hydrogen (H) atom = 1
So, total number of Valence electrons in C3H8 molecule = 4(3) + 1(viii) = xx
Step #2: Select the eye atom (H is always exterior)
While selecting the center cantlet, always put the least electronegative cantlet at the center.
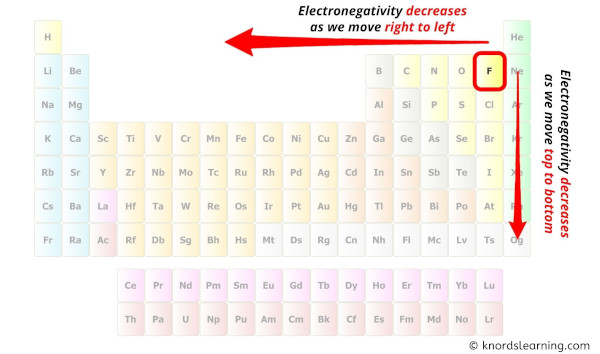
(Remember: Fluorine is the most electronegative chemical element on the periodic tabular array and the electronegativity decreases as we move right to left in the periodic table likewise every bit top to bottom in the periodic table).
Here in the C3H8 molecule, if we compare the carbon atom (C) and hydrogen atom (H), then hydrogen is less electronegative than carbon. Just equally per the dominion, we accept to keep hydrogen outside.
So, all the 3 carbon atoms should be placed in the center and the remaining 8 hydrogen atoms will surround it.
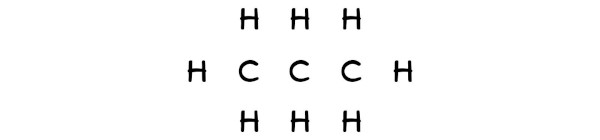
Step #three: Put 2 electrons between the atoms to represent a chemic bond
Now in the above sketch of C3H8 molecule, put the two electrons (i.e electron pair) betwixt carbon-carbon atoms as well as between each carbon and hydrogen atom to represent a chemical bail between them.
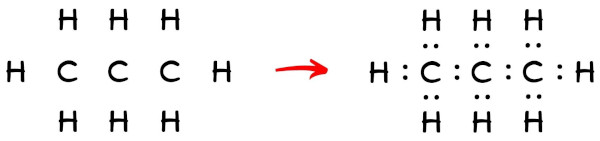
These pairs of electrons present between the Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) atoms form a chemical bond, which bonds the carbon-carbon atom and carbon-hydrogen atoms in a C3H8 molecule.
Step #4: Complete the octet (or duplet) on outside atoms. If the valence electrons are left, then put the valence electrons pair on the primal atom
Don't worry, I'll explicate!
In the Lewis structure of C3H8, the outer atoms are hydrogen atoms.
So now, you lot have to check whether these hydrogen atoms are forming a duplet or non! (considering hydrogen requires only two electrons to have a complete outer vanquish).

You tin can come across in the in a higher place image that all the hydrogen atoms grade a duplet.
Also, all the 20 valence electrons of C3H8 molecule (as calculated in step #ane) are used in the higher up structure. And so at that place are no remaining electron pairs.
Hence there is no modify in the above sketch of C3H8.
Permit'southward move to the side by side pace.
Stride #v: Check whether the central atom has octet or non
In this step, we have to check whether the central atoms (i.e three carbon atoms) have an octet or not.
In simple words, we accept to check whether the central Carbon (C) atoms has 8 electrons or non.
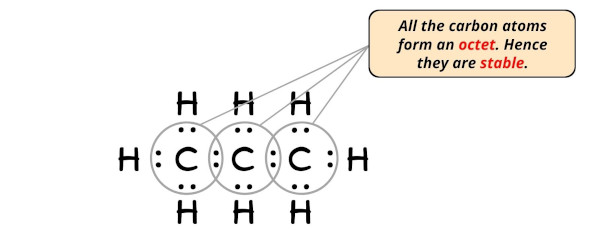
As y'all can come across from the above paradigm, the central atoms (i.e carbon), has 8 electrons. So it fulfills the octet rule and all the carbon atoms are stable.
Step #6: Terminal step – Cheque the stability of lewis structure by computing the formal charge on each atom
Now, you have come to the terminal step and hither you have to cheque the formal charge on each carbon cantlet (C) as well every bit each hydrogen cantlet (H).
For that, you lot need to call up the formula of formal accuse;
Formal charge = Valence electrons – Nonbonding electrons – (Bonding electrons)/2
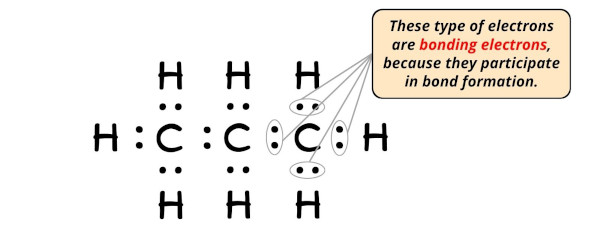
- For Carbon:
Valence electrons = 4 (as it is in grouping 14)
Nonbonding electrons = 0
Bonding electrons = 8 - For Hydrogen:
Valence electron = 1 (every bit it is in group ane)
Nonbonding electrons = 0
Bonding electrons = 2
| Formal charge | = | Valence electrons | – | Nonbonding electrons | – | (Bonding electrons)/2 | ||
| C | = | 4 | – | 0 | – | viii/2 | = | 0 |
| H | = | i | – | 0 | – | 2/ii | = | 0 |
So you can come across above that the formal charges on carbon as well as hydrogen are "zero".
Hence, there will not exist whatsoever change in the above structure and the in a higher place lewis structure of C3H8 is the final stable structure only.
Each electron pair (:) in the lewis dot structure of C3H8 represents the unmarried bail ( | ). And so the to a higher place lewis dot construction of C3H8 can also be represented as shown below.
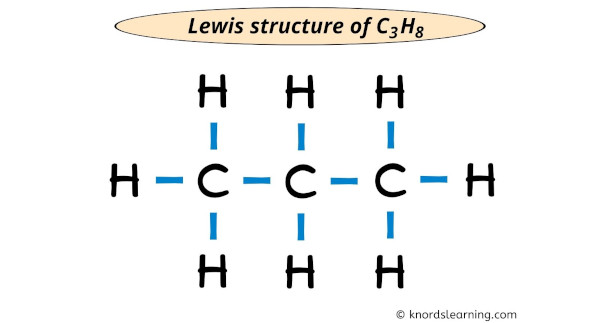
Related lewis structures for your practice:
Lewis Structure of CH3CN
Lewis Structure of SF3-
Lewis Construction of CH3Br
Lewis Construction of CH3OCH3
Lewis Structure of HCOOH (Formic acid)
Lewis Dot Structure For C3h4,
Source: https://knordslearning.com/lewis-structure-of-c3h8-propane/
Posted by: pipesglikeltas.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Lewis Dot Structure For C3h4"
Post a Comment