Incremental Or Differential Costs Are
Costs may be classified as differential toll, opportunity cost and sunk cost. This classification is fabricated for conclusion making purposes. Caption and examples of differential, opportunity and sunk costs are given below:
Differential cost:
The work of managers includes comparison of costs and revenues of different alternatives. Differential price (likewise known as incremental cost) is the difference in cost of ii alternatives. For instance, if the cost of alternative A is $x,000 per yr and the price of alternative B is $8,000 per year. The difference of $2,000 would be differential toll. The differential cost can be a fixed cost or variable cost.
Similarly the difference in revenue of two alternatives is known every bit differential acquirement. For case, if culling A's acquirement is $fifteen,000 and alternative B's revenue is $ten,000. The difference of $5,000 would exist differential revenue.
When unlike revenue generating alternatives are compared, the differential cost as well every bit differential revenues associated with each alternative is taken into business relationship.
The terms "differential cost" and "differential acquirement" used in managerial accounting are similar to the terms "marginal cost" and "marginal revenue" used in economics.
Example – computation of differential cost, differential revenues and differential cyberspace operating income:
The direction of Milky way company has two alternatives to choose from. Compute differential revenue, differential price and differential net operating income from the information of two alternatives given beneath:
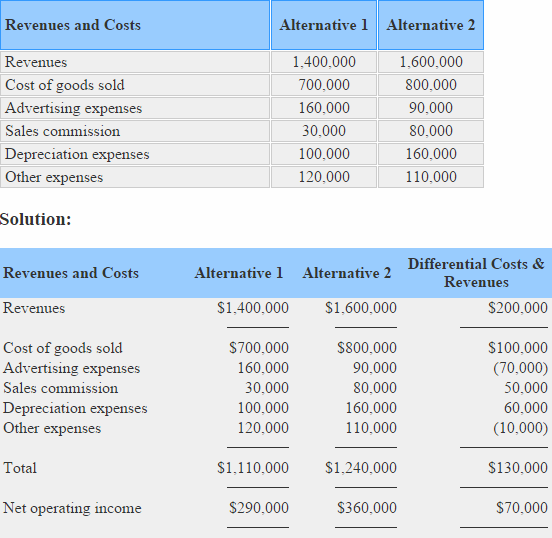
In the above example, total differential revenue is $200,000 (i,600,000 – 1,400,000), differential cost is $130,000 (i,240,000 – 1,110,000) and differential cyberspace operating income is $70,000 ($360,000 – $290,000).
If a determination is made on the basis of above computations, alternative ii would be selected because information technology promises to generate more net operating income.
Opportunity cost:
Unlike other types of cost, opportunity cost does not require the payment of cash or its equivalent. Information technology is a potential benefit or income that is given up as a result of selecting an culling over another. For instance, Y'all have a job in a company that pays you $25,000 per year. For a meliorate futurity, yous desire to get a Master's caste but cannot continue your job while studying. If you determine to give up your chore and render to schoolhouse to earn a Master'due south degree, you would non receive $25,000. Your opportunity cost would exist $25,000.
Almost every alternative has an opportunity cost. Information technology is non entered in the accounting records but must exist considered while making decisions.
Sunk toll:
The costs that have already been incurred and cannot exist changed by any decision are known as sunk costs. For example, a company purchased a machine several years ago. Due to change in fashion in several years, the products produced past the machine cannot exist sold to customers. Therefore the machine is at present useless or obsolete. The price originally paid to purchase the machine cannot be recovered by whatever action and is therefore a sunk cost.
Sunk costs should non be taken into account while making any decision because no action can revers them.
More from Classifications of cost (explanations):
Incremental Or Differential Costs Are,
Source: https://www.accountingformanagement.org/differential-opportunity-and-sunk-costs/
Posted by: pipesglikeltas.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Incremental Or Differential Costs Are"
Post a Comment